Decentralized Autonomous Organizations, or DAOs, are revolutionizing the way we think about businesses and organizations in the digital era. Imagine a soccer club where each member has an equal voting power that influences all decisions fairly. It is this democratic model on which DAOs are founded, redefining organizational governance through blockchain.
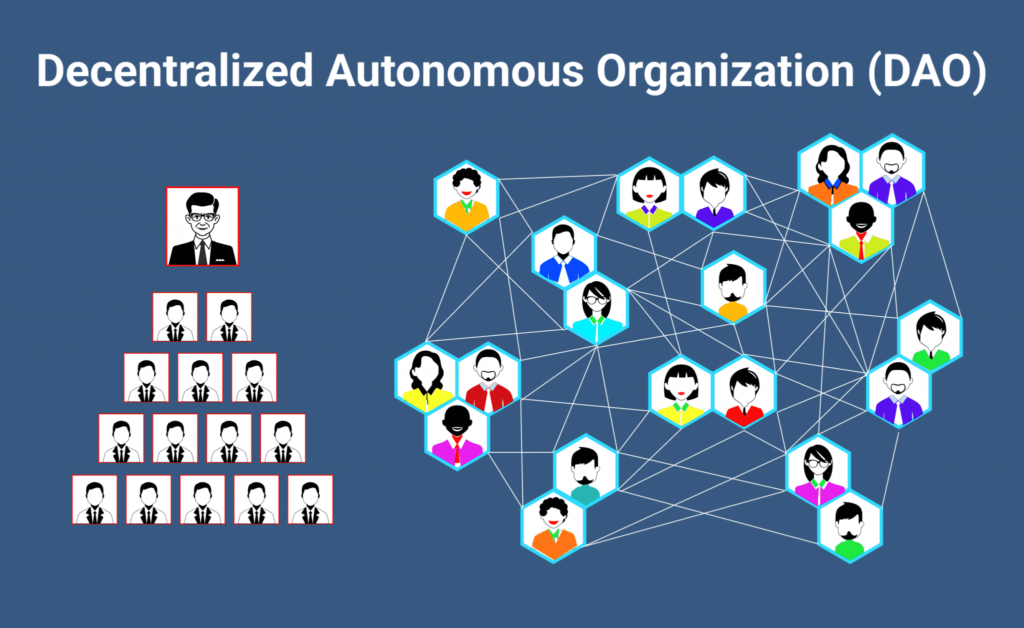
Definition of DAOs
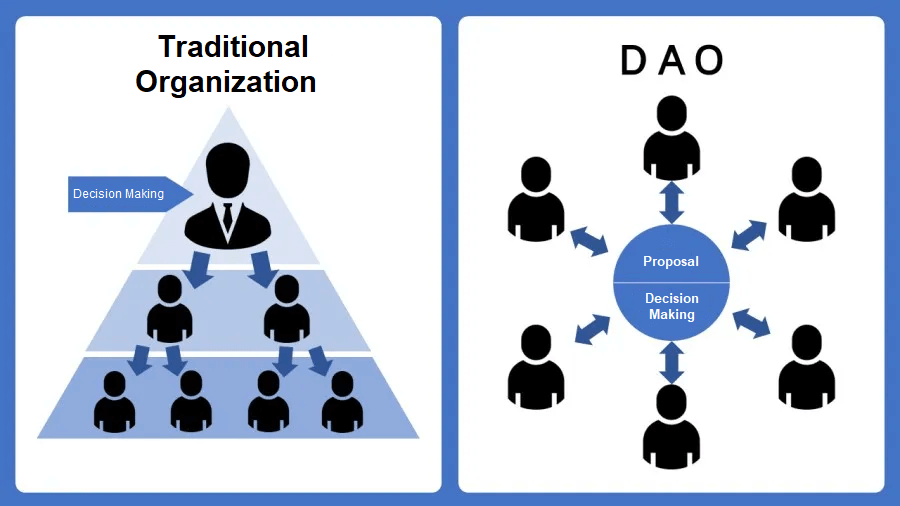
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations, or DAOs, operate via computer code, including smart contracts, which automate operations transparently without the need for a central authority. Unlike traditional organizational models based on hierarchies and manual processes, DAOs establish a structure where decisions are made collectively. Thanks to blockchain technology, every member can participate in significant decisions through a voting system, ensuring unparalleled democracy and transparency.
Advantages: The Strengths of DAOs
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) offer a multitude of advantages that could revolutionize the way we conceptualize and manage organizations:
- Democracy and Transparency: DAOs operate on principles of shared governance, where each member has a voice. Decisions are made collectively, ensuring maximum transparency and fairness.
- Reduction of Human Interference: By automating processes through smart contracts, DAOs minimize human errors and manipulation, leading to more efficient and impartial management.
- Global Accessibility: Anyone with an internet connection can participate in a DAO, breaking down geographical and economic barriers and enabling global collaboration.
- Resilience and Security: DAOs are hosted on blockchain networks, offering security against attacks and resistance to censorship.
- Innovation and Agility: The flexible structures of DAOs encourage innovation, allowing for quick adaptation to changes and new opportunities.
- Cost Reduction: By eliminating intermediaries and automating management, DAOs can operate at a significantly lower cost than traditional organizations.
These advantages position DAOs as potential catalysts for change across various sectors, promoting more inclusive, equitable, and efficient organizational models.
Challenges Facing DAOs
Despite their transformative potential, Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) encounter several critical challenges. Firstly, their decentralized nature raises questions about regulation and legal compliance in a world where legal frameworks are primarily designed for centralized entities. Additionally, while blockchain systems are robust, they are not infallible, and DAOs can be vulnerable to cyberattacks or flaws in their smart contracts.
Governance is also a major issue: how can we ensure fair and effective participation of all members, prevent the concentration of power, and make decisions in the common interest?
Furthermore, the question of interoperability with other systems and ease of use for the general public remains an obstacle to be overcome for DAOs to fully realize their potential. This method creates an ecosystem where trust is established not by a central authority but through fair collaboration and competition among participants, thereby enhancing the integrity and reliability of the blockchain for all its users.
Technical Aspect: The Mechanics of DAOs and Tokens
DAOs are built on innovative technical foundations, with a particular focus on governance tokens. These tokens are central to the operation of DAOs, enabling democratic participation and decentralized management.
Governance tokens are essential in DAOs, as they give their holders the right to vote on important proposals, thus influencing the direction and decisions of the DAO. This includes strategic decisions, rule changes, or the allocation of financial resources. These tokens ensure that each voice counts and that decisions are made collectively, reflecting the interests of the community.
Voting Mechanisms
The voting process in a DAO is facilitated by smart contracts on the blockchain. Holders of governance tokens can submit their votes on various proposals, with a system that ensures transparency and fairness. The weight of the vote is often proportional to the number of tokens held, giving more influence to participants who are most invested in the DAO.
Implications of Governance Tokens
Holding governance tokens implies active participation in the life of the DAO. It allows members to actively shape the future of the organization, its projects, and its initiatives. It is a form of ownership and engagement that goes beyond simply holding assets, providing a voice in key decisions.
Case Study: MakerDAO
MakerDAO is an emblematic example of a successful application of a DAO in the field of decentralized finance (DeFi). This project perfectly illustrates how a DAO can operate and influence the traditional financial sector through blockchain innovation.

What is MakerDAO?
MakerDAO is a DAO that manages the DAI $ token, a stablecoin whose value is pegged to the dollar. This system allows for the creation of DAI by pledging digital assets in smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain. The goal of MakerDAO is to provide a stable and decentralized currency that can be used in the global economy, offering an alternative to traditional fiat currencies.
How MakerDAO Operates
The operation of MakerDAO relies on complex smart contract mechanisms. Users pledge digital assets such as Ether (ETH) to generate DAI.
Impact of MakerDAO
MakerDAO has had a significant impact on the world of decentralized finance by demonstrating that it is possible to create and manage a stable currency without the intervention of central banks or other financial intermediaries. This opens the door to new possibilities in the financial sector, where transparency, security, and financial inclusion are at the forefront.
The system is designed to maintain the stability of DAI against market fluctuations through a participatory governance system. Holders of the governance token, the $MKR token, vote on important decisions such as interest rate adjustments and policy changes to ensure the stability of DAI.
Explore DAOs by Sectors :
- Media and Journalism
- Investment and Finance
- Community and Societal Governance
- Nonprofits and Charitable Projects
- Social Networks and Online Communities
- Education and Research
- Art and Culture
- Technology and Software Development
- Health and Wellness
- Environment and Sustainability

For a deeper exploration of DAOs in these areas, visit : https://daocentral.com
Conclusion:
Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs) mark the beginning of a new era in corporate governance, collaboration, and innovation. By democratizing access to decision-making and providing unprecedented transparency, DAOs have the potential to transform numerous sectors. From investment to art, through education and sustainability, these innovative structures pave the way for more equitable, inclusive, and adaptive projects to the challenges of the 21st century.
As we continue to explore and innovate in the DAO space, it becomes increasingly clear that collaboration and community will be at the heart of future successes. The DAO journey is just beginning, and everyone has a role to play in this revolution.


