LayerZero, a major breakthrough in the world of blockchains, stands out as a revolutionary interoperability protocol. Its aim: to seamlessly and securely connect blockchains. In a landscape where blockchain isolation is the norm, LayerZero emerges as a solution offering the potential for direct interactions between different networks. This in-depth exploration will delve into the fundamentals, solved challenges, ingenious architecture, and future prospects of LayerZero.

Foundations of LayerZero
🔹 Main Mission: Connecting Blockchains
LayerZero stands with a clear mission: to establish bridges between different blockchains. Its fundamental goal is to ensure interoperability, thereby allowing blockchains to communicate seamlessly with each other. By breaking traditional barriers, LayerZero aims to create an ecosystem where inter-blockchain communication becomes the norm.
🔹 Messaging Protocol
At the core of LayerZero lies its status as a messaging protocol. This feature positions LayerZero as an essential infrastructure, providing a solid foundation upon which applications can thrive. By facilitating efficient communication between blockchains, this protocol eliminates costly validation hurdles while opening the door to a wide range of inter-chain functionalities.
🔹 Introduction of Omnichain DApps (ODApps)
The major innovation introduced by LayerZero is Omnichain DApps (ODApps). This new generation of decentralized applications surpasses the limitations of traditional DApps, allowing developers to create inter-chain applications with the ease comparable to that of a single blockchain, whether it be Ethereum, Polygon, or other networks.
Thanks to LayerZero’s architecture, ODApps leverage liquidity present across various networks without requiring trusted intermediaries or consensus protocols.
Current Challenges and Solutions Provided by LayerZero
🔹 Liquidity Fragmentation in Multi-Chain DEXs
Liquidity fragmentation is a challenge faced by multi-chain decentralized exchanges (DEXs). Currently, when DEXs operate across multiple chains, they are constrained to divide their liquidity among these different networks.
➮ For example, DEXs like TraderJoe and SushiSwap, although active across multiple chains, face the challenge of not having sufficient volumes and TVL to compete with native DEXs on each chain.
LayerZero provides an innovative solution to this fragmentation by allowing DEXs to use only one interface and a set of pre-written codes for each pair between two chains. Thus, liquidity is no longer fragmented, offering an enhanced user experience by avoiding exorbitant fees, slippage, and other obstacles associated with fragmentation.
🔹 Challenges for Developers in a Multi-Chain Environment
Developing applications in a multi-chain environment proves to be a real headache for developers. Synchronizing token smart contracts across different networks requires programming in diverse languages, with specific characteristics and security steps to follow on each network. As DApps integrate more networks, this complexity increases, exposing applications to hacking risks, additional costs, and cumbersome management.
LayerZero simplifies this challenge by allowing DEXs to use only one interface and a set of pre-written codes for each pair between two chains. This modular approach streamlines the development process in a multi-chain environment, offering developers an efficient solution to overcome challenges related to blockchain diversity.
🔹 Role of Oracle and Relays in Security and Interoperability
To ensure security and interoperability, LayerZero integrates the concepts of Oracle and Relays into its architecture. Oracles, such as Chainlink (@chainlink) and Band Protocol (@BandProtocol), are essential for extracting block headers from one chain and transmitting them to another. Similarly, Relays work by retrieving proof of a specific transaction.
The network’s security depends on the honesty of these two parties. If the Oracle and Relay act honestly, the transaction is validated and transmitted to the target chain. However, LayerZero recognizes the potential vulnerability when both parties become “dishonest” simultaneously, which could lead to malicious collusion. To mitigate this risk, LayerZero implements a “valid delivery” mechanism, where each message is associated with a transaction on the original chain, ensuring secure and reliable inter-chain communication.
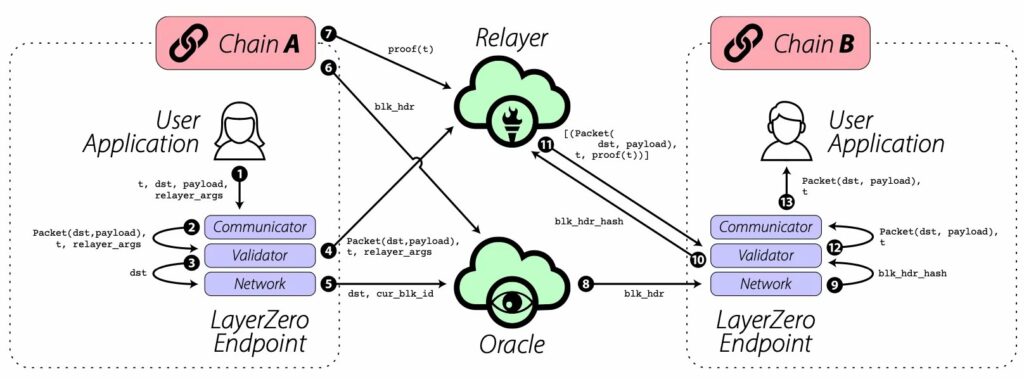
Architecture of LayerZero
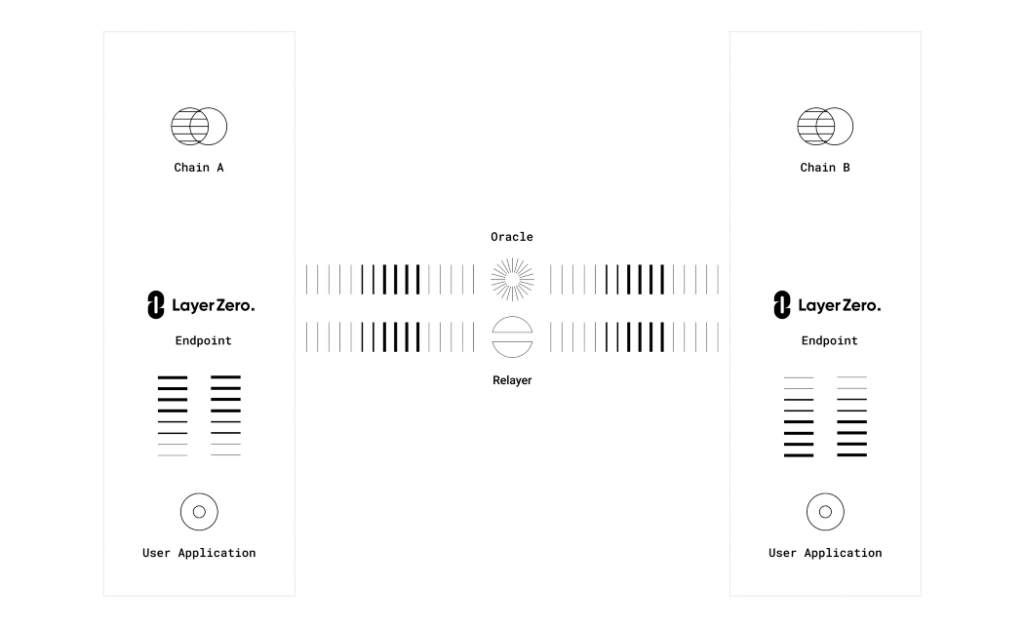
🔹 Endpoints as User Interface
LayerZero’s “Endpoints” serve as the essential user interface on each network. Comprising the Communicator, Validator, Network, and Libraries, these Endpoints ensure the basic functionality of the protocol. LayerZero’s modular design allows for the easy addition of new chains without altering existing modules, thus providing remarkable flexibility.
🔹 Operation in 3 Steps: Communicator > Validator > Network
The process of sending and receiving messages on LayerZero revolves around three steps. On the sender’s side, messages follow the order: Communicator > Validator > Network. This sequence ensures the consistency and verification of transmitted information. On the recipient’s side, messages are received in the reverse order: Network > Validator > Communicator. This methodology guarantees efficient bidirectional communication between different networks.
🔹 Integration of New Chains through Libraries
➮ Each new chain added to LayerZero integrates by extending the existing libraries. These libraries, in the form of auxiliary smart contracts, define the communication standards of each chain.
➮ Each network has its own library, and each Endpoint retains a copy of each library. Thus, communication between two chains becomes possible as soon as they have their respective libraries at both ends.
➮ This modular and extensible approach makes integrating new chains as simple as updating a library, contributing to the flexibility and scalability of LayerZero.
Integration of Cosmos’s IBC (Inter-Blockchain Communication)
🔹 Limitations of IBC
While Cosmos’s IBC is robust for connecting internal zones within the Cosmos ecosystem, it faces limitations when extending to external networks such as Ethereum or other EVM-based ones. These limitations often arise due to the need for a full light client to connect two chains, which becomes costly, especially for widely used EVM networks like Ethereum.
🔹 Using IBC in LayerZero for Broader Communication
LayerZero has addressed these challenges by strategically integrating Cosmos’s IBC. Instead of strictly adhering to the IBC’s transport layer, LayerZero has replaced it with its own transport layer. Thus, the IBC can now reach all chains connectable through LayerZero via its transport layer.
➮ This innovation eliminates constraints related to the need for a full light client for each chain pair, making inter-chain communication more accessible and cost-effective.
🔹 Advantages of LayerZero’s Approach over IBC Alone
LayerZero’s approach offers advantages over simple IBC usage. By adopting this approach, LayerZero becomes a bridge between networks, enabling extended communication without sacrificing efficiency and offering an economical solution. Combining the LayerZero transport layer with the IBC significantly expands the scope of interoperability, creating a network that can extend beyond the boundaries of individual ecosystems. This intelligent integration allows LayerZero to leverage IBC standards while overcoming its restrictions, shaping a more fluid and connected inter-chain landscape.
Detailed Operation of LayerZero
🔹 Utilization of an Ultra Light Node (ULN)
At the core of LayerZero’s operation is the use of an Ultra Light Node (ULN). This concept ensures transaction validation between different blockchains efficiently. The ULN acts as an ultra-lightweight node, storing only block headers on demand. This streamlined approach ensures fast and efficient communication between networks, thereby eliminating constraints associated with storing full blocks.
🔹 Crucial Role of Oracles (Chainlink, Band Protocol)
Oracles play a central role in the LayerZero ecosystem, acting as decentralized bridges between different blockchains. See part 2 of this thread for more details.
🔹 Importance of Relayers in the Interoperability Process
The Relayer, another essential component of the interoperability process, operates similarly to the Oracle but with a specific mission. We’ve also discussed this in part 2.
In summary, LayerZero’s operation relies on a combination of ULN, Oracles, and Relayers, thus providing a robust solution to overcome challenges related to interoperability between blockchains. This approach ensures the fluid exchange of information and assets while maintaining a high level of security and trust within the LayerZero ecosystem.
Characteristics and Advantages of LayerZero
🔹 Trustless System and its Impact on Security
LayerZero distinguishes itself with its Trustless system, eliminating the need for trust between parties. Unlike other interoperability protocols that rely on centralized intermediaries, LayerZero relies on independent Oracles and Relayers. This approach enhances the security of inter-chain transactions, minimizing risks associated with trusted third parties. By adopting a trustless logic, LayerZero embodies the essence of blockchain, ensuring increased reliability in its DECENTRALIZED exchanges.
🔹 Modular and Scalable Architecture
LayerZero’s architecture is a model of flexibility and scalability. Operating on a modular principle, the protocol allows for easy integration of new blockchains and functionalities without disrupting the core of the system. This modularity gives LayerZero unparalleled agility, facilitating seamless deployment of updates.
Compared to other protocols requiring complex modifications for each addition, LayerZero offers a scalable approach, tailored to the constantly evolving needs of the blockchain ecosystem.
🔹 Optimized User Experience with Low Transaction Fees
LayerZero is committed to providing a smooth and cost-effective user experience. By simplifying the process of sending and receiving tokens with a single transaction, the protocol eliminates unnecessary friction. Additionally, its relatively low transaction fees enhance its attractiveness to users.
This combination of operational efficiency and reduced costs positions LayerZero as an attractive solution, both for developers creating inter-chain applications and for users seeking seamless interaction with multiple blockchain networks.
Advantages and Disadvantages of LayerZero
Its only weakness is that it’s too strong. Just kidding, there are still a few drawbacks, otherwise this section wouldn’t exist!
🔹 Strengths of the Protocol
➮ Trustless System
LayerZero stands out with its trustless approach, eliminating the need to trust third parties. This feature enhances the security of inter-chain transactions, ensuring the integrity of exchanges without relying on centralized parties. We’ve seen this in part 7.
➮ Efficiency and Cost Minimization
LayerZero’s efficiency translates into simplified inter-chain transactions in a single step, reducing associated fees and frictions. This cost savings makes LayerZero an attractive solution for users and developers seeking cost-effective interoperability.
➮ Flexibility with a Single Endpoint
Using a single Endpoint as a user interface simplifies interaction with LayerZero. This streamlined approach offers a consistent user experience and reduces complexity, facilitating the protocol’s adoption by a wide range of users.
🔹 Weaknesses and Challenges
➮ Lack of Adoption
Although promising, LayerZero must overcome the challenge of lack of adoption. Being relatively new to the market, the protocol must make efforts to raise awareness and attract users, developers, and blockchain projects. It would be cool if they integrated networks like Solana (@solana $SOL).
➮ Potential Bug Risks
Like any protocol under development, LayerZero faces the risk of bugs. Development teams must be vigilant and identify and promptly resolve any issues, ensuring the stability and reliability of the system.
➮ Competition with Protocols
LayerZero operates in a competitive environment. Convincing industry players of the value and superiority of LayerZero over better-known solutions is a crucial challenge for its widespread adoption.
🔹 Some competitors:
➮ Wormhole: https://wormhole.com
➮ Axelar: https://axelar.network
➮ Hyperlane: https://hyperlane.xyz
LayerZero, by facilitating communication between different blockchains, appears promising with forthcoming enhancements. Interoperability, crucial for the future of blockchains, fosters adoption and global collaboration. As a trailblazer, LayerZero offers an advanced solution, opening the door to new opportunities and contributing to the future of distributed ledger technologies.


