In the ever-evolving world of cryptocurrencies, the Kaspa project stands out by seeking to redefine Proof of Work (PoW). Faced with debates sparked by Proof of Stake, Kaspa emerges with a unique perspective. From its design to its hybrid models like BlockDAG and GhostDAG, Kaspa offers a scalable solution to blockchain challenges while retaining the fundamental principle of PoW. Let’s take a closer look.

𝗪𝗵𝗮𝘁 𝗶𝘀 𝗞𝗮𝘀𝗽𝗮 (𝗞𝗔𝗦)?
🔹 Scalability and Performance-Oriented Design
➮ Kaspa, akin to Bitcoin, emerges as a response to the scalability and performance challenges facing many PoW blockchains.
➮ Its architecture combines the benefits of linear blockchains with DAG innovations, opening up new possibilities for scalability.
🔹 BlockDAG Hybrid Model Combining Linear Blockchains and DAG
Kaspa’s hybrid model, called BlockDAG, merges classical blockchain concepts with DAG features. This promising approach offers a scalable solution while remaining within the realm of PoW.
𝗧𝗵𝗲 𝗡𝗮𝗸𝗮𝗺𝗼𝘁𝗼 𝗖𝗼𝗻𝘀𝗲𝗻𝘀𝘂𝘀
🔹 Fundamental Mechanism
The Nakamoto consensus, named after the pseudonymous creator of Bitcoin, Satoshi Nakamoto, constitutes the central mechanism used in blockchain systems.
🔹 Mining and Intrinsic Value
It involves energy expenditure (mining) to solve cryptographic problems, thereby bringing value to newly mined cryptocurrencies.
🔹 Block Selection
Blocks are selected by favoring the longest chain in case of divergence, while scarcity is maintained by a limit on possible crypto in the market.
🔹 Basis of Bitcoin’s Initial Success
Although resource-intensive, this mechanism was the basis of Bitcoin’s initial success and continues to be advocated for and used by new projects. Kaspa retains this mechanism while making modifications to make it more scalable.
𝗧𝗵𝗲 𝗕𝗹𝗼𝗰𝗸𝗗𝗔𝗚
🔹 Linear Blockchain vs DAG
The linear blockchain, a pillar of many cryptocurrencies, is characterized by a continuous and ordered sequence of linked blocks. In contrast, the DAG offers multiple possible paths, enabling transaction parallelization.
🔹 Transaction Parallelization
Transaction parallelization in the DAG, unlike linear blockchains, enhances the network’s ability to process a large number of transactions simultaneously.
🔹 Transaction Confirmation
New transactions link to multiple previous transactions, and confirmation occurs as soon as a new transaction attaches to them.
🔹 Potential Issues
However, problems may arise when confirming multiple transactions simultaneously or during network latency spikes.
Bitcoin vs Kaspa
🔹 Main Chain Selection
➮ Bitcoin: Relies on the longest chain as the main one, encouraging miners to work on this chain to secure the network, which can lead to forks.
➮ Kaspa: Uses GhostDAG, favoring the heaviest branch in terms of transaction weight, ensuring increased security and adaptation to the needs of modern digital ecosystems.
🔹 Branches and Sub-Branches
➮ Bitcoin: Focuses on the linear main chain.
➮ Kaspa: Introduces the concept of branches and sub-branches in GhostDAG, promoting greater transaction parallelization and offering increased resilience against potential attacks.
🔹 Reducing “Orphan” Blocks
➮ Bitcoin: Faces the issue of orphan blocks when two miners simultaneously solve a similar block.
➮ Kaspa: Thanks to DAG, allows blocks to coexist without being rejected, avoiding resource wastage and strengthening the robustness of the PoW network.
🔹 DAGKnight Protocol
➮ Kaspa: By developing DAGKnight, a new version of DAG, to address issues of network communication slowdown and enhance security against 51% attacks.
🔹 Pruning Mechanism
➮ Kaspa: Introduces the pruning mechanism to optimize the size of the blockchain ledger, improving storage and bandwidth efficiency.
DAGKnight Protocol
🔹 Latency Issue
Latency fluctuations can create delays in transaction confirmation. 📈
🔹 51% Attacks and Latency Spikes
In the context of 51% attacks, latency spikes lower the threshold needed for malicious actors to gain control of the majority of the network nodes.
🔹 DAGKnight: Dynamic Solution
This protocol dynamically adjusts confirmation times in real-time, quickly adapting the network to latency spikes and enhancing security against 51% attacks.
🔹 Enhanced Security
DAGKnight increases security by reducing the time needed to confirm blocks, thereby limiting the window of opportunity for malicious attacks.
Pruning Mechanism
🔹 Resource and Storage Space Optimization
Kaspa has introduced the pruning mechanism to optimize the size of the blockchain ledger while preserving data integrity. (It’s like a kind of file compression on your computer)
🔹 Pruning Nodes and Archiving
Pruning involves reducing the size of the ledger by removing obsolete historical data. Pruning nodes only retain essential data, thus promoting more efficient use of storage space and bandwidth.
🔹 Continuous Participation of Pruning Nodes
Pruning nodes, despite being light in footprint, continue to participate as validators in the network. This approach facilitates resource distribution and encourages participation from users with limited storage capacities.
Introduction to Kaspa Cryptocurrency: $KAS
🔹 A Community Project without Central Authority
Kaspa ($KAS) takes inspiration from the Bitcoin ($BTC) model, establishing a community-driven project without the intervention of a central authority.
🔹 Fair Launch and Transparent Distribution
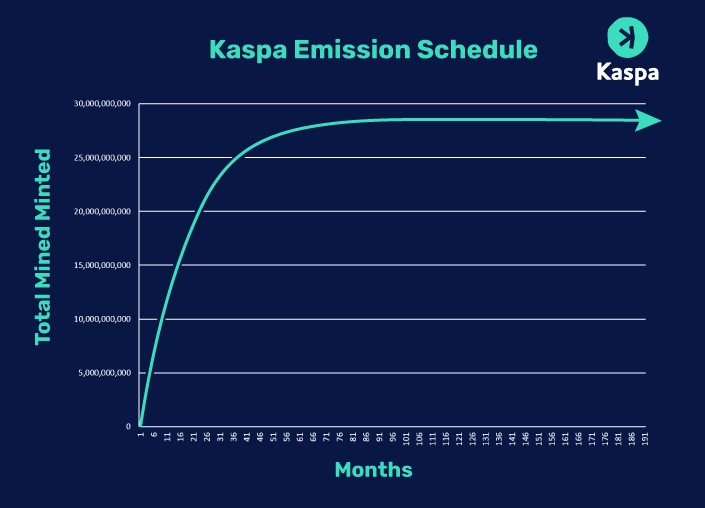
The network mined 21 billion $KAS, with approximately 75% of coins already mined, within a total limit of 28.7 billion. The fair launch avoided favoritism and pre-mining, ensuring transparent distribution.
🔹 Planned Emission Trajectory
The emission trajectory of $KAS, planned until April 2038, includes initial inflation phases followed by “chromatic halvings,” gradually reducing the annual emission. This plan extends over more than 15 years after the Genesis block mining (= very first block).
🔹 Strong Foundations for a Democratic Future
By emphasizing transaction parallelization, energy efficiency, and equitable distribution of computing power, Kaspa presents a project that can serve as an example for the future of PoW-based blockchains.
🔹 Included in this thread are details about Kaspa $KAS tokenomics.
Conclusion
🔹 Innovation in Proof of Work
The Kaspa project offers an innovative approach by combining the advantages of linear blockchains with DAG innovations. The BlockDAG, GhostDAG, and DAGKnight hybrid models appear promising for improving network scalability and security.
🔹 Commitment to Serious Blockchain
The use of the kHeavy Hash algorithm for mining, the pruning mechanism, and active community participation through KIPs demonstrate Kaspa’s commitment to developing a serious and democratic blockchain.
🔹 Towards the Future with Smart Contracts
The team is working on integrating smart contracts, an evolution that could significantly advance the project.
🔹 A Project to Watch
By focusing on transaction parallelization, energy efficiency, and equitable distribution of computing power, Kaspa offers an intriguing vision for the future of PoW blockchains.