Discover how smart contracts, a major innovation made possible by blockchain technology, are revolutionizing the way agreements are formed, executed, and verified in the digital world, without the need for intermediaries.

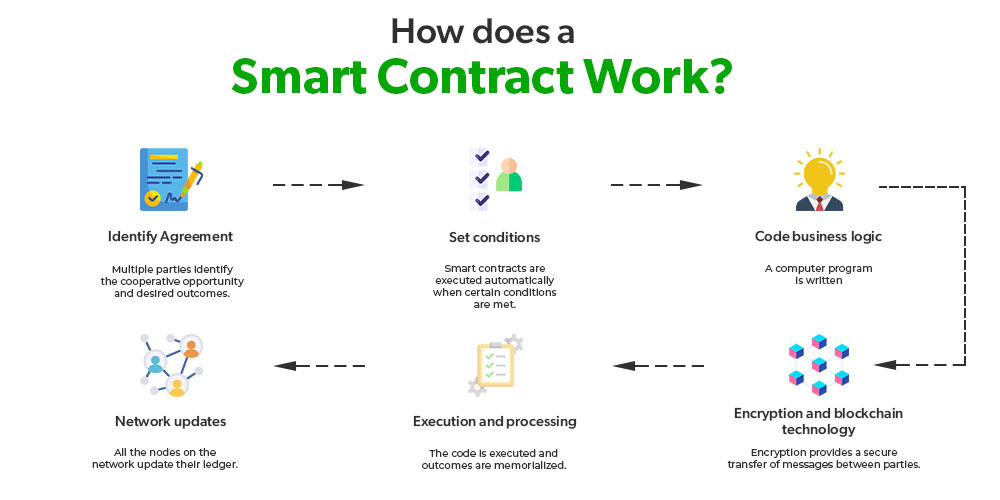
How Does a Smart Contract Work?
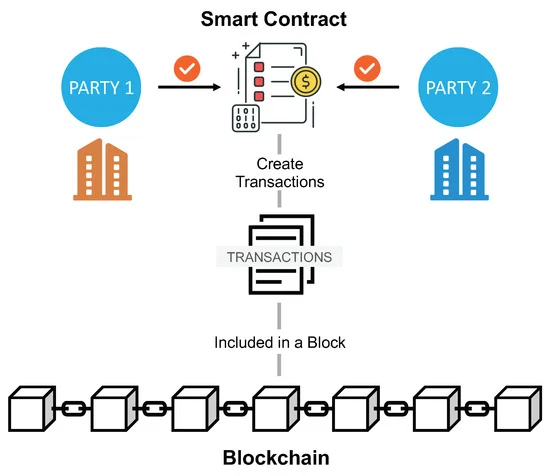
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. Stored on a blockchain, they automatically execute transactions and enforce agreements when predefined conditions are met. This automation ensures that transactions are carried out efficiently and transparently, without the need for intermediaries, thereby reducing the potential for disputes and increasing trust and reliability in digital transactions.
Execution Process
- Triggering Conditions: Just like selecting and paying for a drink triggers the release from a vending machine, in smart contracts, certain conditions such as a payment or the receipt of information trigger contract execution.
- Automatic Execution: Once the conditions are met, the contract automatically executes according to the coded terms. This could involve transferring funds, recording an asset, or any other programmed action.
- Recording on the Blockchain: All transactions and outcomes are securely and immutably recorded on the blockchain, ensuring transparency and traceability.
Smart contracts reduce friction, increase efficiency, and enhance security in digital transactions, opening up new avenues in almost every conceivable sector. By eliminating the need for intermediaries, they promise a more direct and transparent economy.
Advantages of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts transform how transactions and agreements are executed, offering significant benefits in terms of transparency, security, and efficiency.
Transparency and Reduction of Intermediaries
Thanks to blockchain, smart contracts ensure absolute transparency. Each party can verify the terms and execution of the contract because they are recorded immutably. This eliminates the need for intermediaries, reducing the costs and delays often associated with traditional transactions.
Enhanced Security and Efficiency
Smart contracts are secured by blockchain technology, making transactions difficult to compromise provided the smart contract is correctly created. Once the conditions of the contract are fulfilled, execution is automatic, eliminating human errors and significantly speeding up the process. This ensures not only enhanced security but also unprecedented operational efficiency.
While smart contracts are praised for their ability to enhance transaction security, it is crucial to note that this security largely depends on the quality of their creation and implementation. A well-designed contract can offer exceptional security, but if errors are present in the code, it can become vulnerable.
The Importance of Code Audits
To ensure the reliability and security of smart contracts, code audits are essential. These thorough reviews help to detect and correct potential flaws before a contract is deployed on the blockchain. Audits are conducted by security experts who scrutinize the code for vulnerabilities, ensuring that the contract functions as intended and is secured against attacks.
Conditional Security
The security offered by smart contracts is thus conditional on their careful design and rigorous verification. A smart contract that is properly audited and designed according to best practices can significantly reduce the risks of manual errors and fraud, providing enhanced transparency and efficiency in digital transactions.
Use Cases of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts find applications in numerous fields, offering innovative solutions to automate and secure transactions and agreements.
Here are some striking examples:
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): They automate lending, borrowing, and interest calculations, revolutionizing how we interact with financial services.
- Real Estate: In the real estate sector, smart contracts can replace tasks traditionally performed by notaries, such as recording transactions and transferring property ownership, making the process faster and less costly.
- Music Industry: They enable automatic distribution of royalties, ensuring that artists are paid fairly and promptly each time their music is played or downloaded.
- Identity Verification: Smart contracts facilitate secure verification of identities online, improving the reliability of digital transactions.
- Supply Chain: They provide total transparency in the supply chain from production to delivery by indelibly recording each step on the blockchain. These examples illustrate the versatility of smart contracts, capable of bringing efficiency, security, and transparency across various sectors.
Conclusion
While we can send a man into space and pay for coffee in seconds with our phone, it almost seems comical that in 2024, buying a house in France can still feel like an epic, with months of waiting between the sale agreement and the final deed.
This situation underscores a crucial point: blockchain is prompting us to rethink our traditional processes. For sectors like real estate, it’s decision time: either adapt by integrating technologies such as smart contracts to speed up and secure transactions or risk becoming obsolete.
Notaries, and other professionals, might find themselves at the forefront of this transformation, developing protocols using smart contracts to modernize the real estate purchasing process. This change could not only save time but also provide increased security and transparency for everyone.
The question is no longer if this transformation will occur, but rather how and when. Smart contracts invite us to envision a future where efficiency, security, and speed are the norm, not the exception!