Discover how Ethereum is redefining the boundaries of blockchain and opening up a world of unprecedented possibilities.

Introduction to Ethereum
In 2013, a 19-year-old prodigy, Vitalik Buterin, published the Ethereum white paper, laying the foundation for a new era in the blockchain universe. Unlike Bitcoin, which was primarily designed as a value transfer system, Ethereum was intended as a platform for deploying smart contracts and decentralized applications (DApps), thereby paving the way for nearly limitless possibilities.

Launched in 2015, Ethereum has revolutionized the blockchain world with its smart contracts, enabling automatic contract execution when certain conditions are met, without the need for intermediaries. Buterin envisioned Ethereum as a global computer capable of changing the way we interact with the digital world.
The contribution of Gavin Wood, co-founder of Ethereum and the first CTO of the Ethereum Foundation, was also crucial. As the developer of the Solidity language and author of the “yellow paper” detailing Ethereum’s technical architecture, Wood played a critical role in the platform’s evolution. Despite sometimes divergent visions, leading Wood to later create Polkadot, their work laid the cornerstone of Ethereum.
Difference Between Ethereum and Bitcoin
If Bitcoin is often compared to digital gold, serving as a store of value, then Ethereum could be likened to silver, a precious metal as well, but with a multitude of practical uses that go beyond mere value conservation.
Objectives and Vision:
- Ethereum: Created by Vitalik Buterin and launched in 2015, Ethereum goes beyond the idea of a simple digital currency. Its vision is to become a global platform for the deployment of smart contracts and decentralized applications (DApps), thus providing a framework for creating any type of blockchain project.
- Bitcoin: Launched by Satoshi Nakamoto in 2009, Bitcoin was primarily designed as a decentralized digital currency. Its goal is to enable secure transactions without the intervention of third parties, thus acting as a digital alternative to fiat currency.
Unlike Ethereum, whose genesis and development were openly shared by its founder Vitalik Buterin, Bitcoin has an origin shrouded in mystery. Apart from the pseudonym of its creator, Satoshi Nakamoto, the true identity of the person or group behind Bitcoin is unknown. This enigma reinforces the decentralized and independent nature of Bitcoin, emphasizing the idea that it truly belongs to everyone, without a central figure of power.
If Bitcoin has traditionally been seen primarily as a store of value, it is important to emphasize that recently, ambitious initiatives have begun to emerge, aiming to extend its functionalities beyond this initial use. Among these innovations are Ordinals, BRC-20, and projects aimed at developing second-layer (Layer 2) solutions on the Bitcoin blockchain. These developments, previously unimaginable, open new prospects for the use of Bitcoin, suggesting the possibility of creating decentralized applications and other forms of digital interactions directly on its blockchain. These evolutions represent a significant paradigm shift for Bitcoin, marking a potential convergence with Ethereum’s versatility in terms of blockchain applications.
It will be particularly interesting to follow this narrative in the coming years, especially in 2024 and 2025, when these initiatives could significantly transform the perception and use of Bitcoin within the blockchain ecosystem, as well as generate significant gains for those positioned on the right projects building on Bitcoin. Although Ethereum has long dominated the NFT market, Bitcoin is beginning to carve out a place for itself. This development highlights the rapid evolution of the cryptocurrency sector, where innovation opens new paths. This expansion of Bitcoin into NFTs could enrich the cryptocurrency ecosystem, offering more choices to users and new perspectives for investors.
Ethereum Operation
Ethereum represents a major advancement in the universe of blockchain technologies, thanks to its ability to execute smart contracts and host decentralized applications (DApps). At the core of its operation, several key components are found: smart contracts, Ether (ETH), second-layer (L2) solutions, and the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM).
Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are at the heart of Ethereum’s innovation. They enable the creation of self-executing agreements that operate transparently and securely, without the need for a third party. This opens the door to a multitude of applications, from decentralized finance (DeFi) to gaming and beyond.
Ether (ETH)
Ether is the native cryptocurrency of Ethereum, used to reward miners, pay for transaction fees, and cover the execution costs of smart contracts. ETH also serves as the “gas” that powers operations and applications running on the Ethereum blockchain, ensuring their proper function and security.
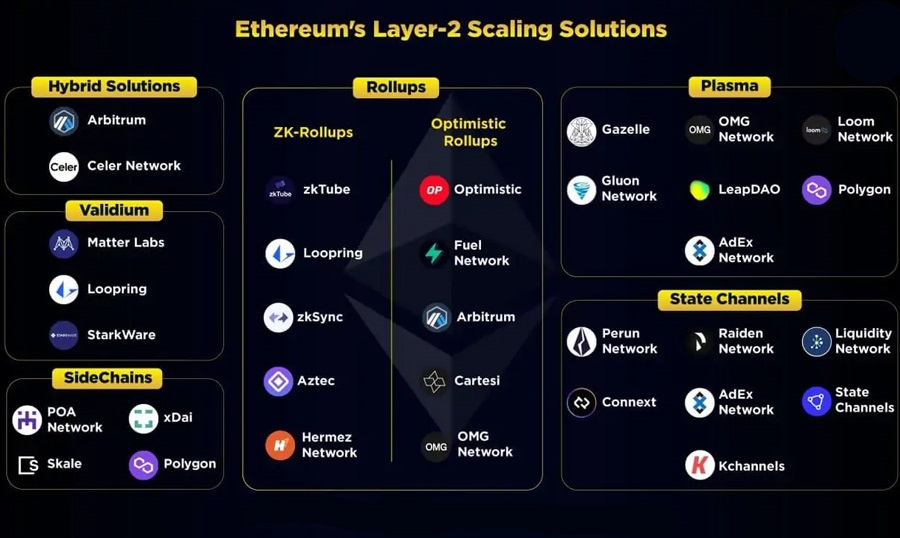
Second-Layer Solutions (L2)
To address the challenges of scalability and transaction costs, Ethereum relies on second-layer solutions. Technologies such as rollups work parallel to the main blockchain to process transactions more efficiently and economically before consolidating the results on the Ethereum blockchain.
Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM)
The EVM is the execution environment for smart contracts on Ethereum. It allows anyone, anywhere in the world, to execute smart contracts securely and in isolation, ensuring that programs function exactly as intended, without any possibility of censorship, fraud, or third-party interference.
Ethereum Evolution and Challenges
The transition of Ethereum to Ethereum 2.0, which marked the shift from the Proof of Work (PoW) consensus mechanism to Proof of Stake (PoS), has recently taken place, representing a significant evolution for the blockchain. Despite the advancements promised by Ethereum 2.0, the blockchain faces several ongoing challenges:
- Scalability: Ethereum’s ability to process transactions quickly and on a large scale remains a challenge. Although the transition to PoS and the introduction of technologies like sharding are steps towards improved scalability, finding the right balance between security, decentralization, and speed is an ongoing challenge.
- Transaction Fees: Gas fees, necessary for executing transactions and smart contracts on Ethereum, can become extremely high during network congestion peaks. This can limit access to the blockchain for certain users and use cases, particularly in the areas of DeFi and NFTs.
- Dencun Update: The Dencun update, marking a significant advancement in the evolution of Ethereum, has been successfully deployed on the mainnet after conclusive tests on the Goerli testnet. This transition marks a key moment as it materializes the anticipated improvements, especially the integration of Proto-Danksharding via EIP-4844. This innovation is intended to revolutionize the efficiency of transactions and applications on Layer 2, significantly reducing costs for developers and users.
- Proto-Danksharding via EIP-4844: At the heart of Dencun lies Proto-Danksharding, introduced by EIP-4844. This innovation specifically targets the issue of high transaction fees by optimizing data management on Layer 2. Temporary data storage on consensus nodes helps to relieve network congestion, thereby reducing costs for users and developers.
With the deployment of Dencun, Ethereum takes another step towards a more scalable, secure, and economically viable network. These technical improvements aim to support the continuous growth of the Ethereum ecosystem by facilitating access and reducing costly barriers for users and developers.
Moreover, it is important to note that following the approval of a Bitcoin ETF, Ethereum could follow this trajectory with a high likelihood of seeing an Ether-based ETF approved during 2024. This step, following that of Bitcoin, would symbolize further recognition of cryptocurrencies in the realm of traditional investments and could have profound impacts on Ethereum’s market dynamics.
Conclusion:
Ethereum remains the second largest player in the cryptocurrency market. Despite numerous speculations about “Ethereum killers,” Ethereum has managed to maintain its dominant position. This resilience is a testament to its influence and value within the blockchain ecosystem. With the advent of Ethereum 2.0 and its upcoming updates, Ethereum continues to be at the forefront of innovation in the field.


