We think you’ve all heard of @arbitrum, the Ethereum Layer 2 currently experiencing the highest activity + TVL in the market. However, are you truly familiar with this project? On the surface, perhaps… But today, we’re going to dive deeper into this initiative, pioneering Layer 2 solutions, which presents itself as an answer to Ethereum’s scalability challenges.

History and Genesis of Arbitrum
🔹 Origin of the Project and Context of Ethereum’s Evolution
Arbitrum has its roots in the context of Ethereum’s evolution, marked by rapid growth but facing scalability challenges we’re all too familiar with (if you’re not, try making a transaction on Ethereum’s mainnet, and you’ll likely understand). The need to address these issues gave rise to innovative initiatives, with Arbitrum emerging as a relevant response.
🔹 Initial Development of Arbitrum by Offchain Labs
Initiated by @OffchainLabs, Arbitrum came into being through the commitment and expertise of Steven Goldfeder, Harry Kalodner, and Ed Felten. This exceptional team, steeped in computer security and blockchain knowledge, laid the groundwork for Arbitrum by exploring potential solutions to Ethereum’s scalability challenges. (We’ll delve into the team in more detail in part 3).
🔹 Inspiration from Sidechains and Layer 2, Particularly Rollup Technology
The development of Arbitrum drew inspiration from concepts of sidechains and Layer 2. The vision of “rollup,” which efficiently bundles a large number of transactions into a single point on the main blockchain, was central to the development process. This approach reconciled scalability with security. In essence, Layer 2 solutions aggregate multiple transactions into “packets” and inject them into the main chain.
Example:
➮ Imagine Layer 1 as a conveyor belt carrying packages from point A to point B. However, this belt has a limited capacity, and if too many packages are placed on it at once, they might fall off. Here’s where Layer 2 comes in, acting as smaller conveyor belts to pick up packages from point A, easing the load on the main belt, Layer 1.
➮ These packages on Layer 2 belts, however, need to reach point B eventually. Hence, a machine on Layer 2 belts groups them into similarly sized packets before placing them back on the main belt, occupying the same space as a regular package. This facilitates the transport of a larger number of packages between point A and point B without overloading the main belt.
ℹ️ Information: For those unfamiliar with what a sidechain is and the difference between a sidechain and L2, we will explain! ➮ A sidechain is a blockchain connected to a main blockchain. It allows specific transactions without burdening the main blockchain. Sidechains are used for specific use cases, improving scalability by offloading the main blockchain’s load and using a bidirectional mechanism to transfer assets between the main blockchain and the sidechain. They offer flexibility while maintaining security. ➮ Sidechains are distinct blockchains connected to a main blockchain, allowing asset transfers between them. Layer 2 solutions operate above the main blockchain to perform off-chain transactions without necessarily transferring assets between chains. Both aim to improve the scalability and efficiency of existing blockchains but use different approaches.
🔹 Need for Scaling Solutions Amid Ethereum’s Scalability Challenges
The Ethereum landscape, plagued by prolonged confirmation times and high transaction fees, has created a growing demand for scaling solutions. Arbitrum has emerged as a strategic response, offering an effective alternative by leveraging the innovative design of “rollup” to significantly address scalability issues.
Architecture of Arbitrum
🔹Utilization of Optimistic Rollup Technology
Arbitrum relies on the advanced technology of Optimistic Rollup, a Layer 2 approach crucial for enhancing performance and reducing costs on the Ethereum blockchain.
ℹ️ Information: We can see you behind your screen, probably wondering what an Optimistic Rollup really is, right? Because yes, we all have a somewhat approximate idea of what it is, but we don’t exactly know what it entails. Don’t worry, we will explain it here. For those who are already familiar, you can skip to the “ℹ️ Information” section.
➮ Optimistic Rollups are a method for managing off-chain transactions while ensuring security on Ethereum. Funds are stored in a smart contract on the main chain, while transactions are aggregated off-chain and published in a condensed manner.
➮ Security relies on a “validity game” between issuers and aggregators. Transactions are aggregated off-chain, and the aggregator’s proposal becomes valid after a seven-day verification period, during which the state root can be recalculated by anyone.
➮ If no disputes occur, the changes are recorded on Ethereum after seven days. In case of dispute, a participant can publish the valid root, reclaiming some of the collateral deposited by the dishonest aggregator. This “optimistic” mechanism ensures network reliability with at least one honest validator.
➮ “Optimistic” in Optimistic Rollup signifies an optimistic approach where it’s presumed that most participants will act honestly. Rather than demanding immediate cryptographic proofs, the system presumes the initial transaction validity, with subsequent verification in case of dispute. The term underscores the initial trust in participants’ integrity.
🔹 Two-Step Transaction Processing Operation
Arbitrum’s operational process adopts a two-step method. Initially, transactions are executed off the main blockchain, in a secondary layer. Then, proof of these transactions is sent to the Ethereum blockchain to finalize the process. This approach optimizes overall processing by consolidating multiple off-chain transactions into a single transaction on the main blockchain (as we saw previously).
🔹 Advantages of the Approach
Arbitrum’s approach offers significant advantages, including a drastic reduction in transaction costs and acceleration of confirmation times. By processing multiple transactions simultaneously off-chain, Arbitrum optimizes efficiency while maintaining the security of the main blockchain.
🔹 Comparison with Other Layer 2 Solutions and Details on Optimistic Rollup Technology
In comparison with other Layer 2 solutions, Arbitrum stands out for its choice of Optimistic Rollup technology, which enables transaction compression, thus reducing gas fees and optimizing block space. However, other solutions like ZK (Zero-Knowledge Proof) Layers 2 exist, for example:
- Starknet (@Starknet)
- Scroll (@Scroll_ZKP)
- ZKsync (@zksync)
The Team Behind Arbitrum
🔹 Profiles of Key Team Members: Steven Goldfeder, Harry Kalodner, Ari Juels
Arbitrum’s leadership team consists of prominent figures such as Steven Goldfeder, CEO of Arbitrum, Harry Kalodner, co-founder and CTO, and Ed Felten, another co-founder. These leaders have combined their expertise to propel Arbitrum to success.
➮ Steven Goldfeder: Holds a Ph.D. from Princeton and is a co-author of the book “Bitcoin and Cryptocurrency Technology”. LinkedIn: Steven Goldfeder
➮ Harry Kalodner: A Princeton graduate with a strong background in economics, cryptocurrencies, and anonymity. LinkedIn: Harry Kalodner
➮ Ed Felten: A leading scientist specializing in cryptography and security, who served as a senior technology advisor at the White House. LinkedIn: Ed Felten
🔹 Team’s Experience and Expertise
The Arbitrum team boasts extensive experience and sharp expertise in crucial areas such as computer security, cryptography, and blockchain research. These skills were vital in developing a solution capable of addressing the scalability challenges posed by Ethereum.
🔹 Commitment to Enhancing the Blockchain Ecosystem and Developing the Arbitrum Solution
The Arbitrum team demonstrates unwavering commitment to enhancing the blockchain ecosystem. Their dedication is evident through the ongoing development of the Arbitrum solution, an innovative project designed to tackle the major scalability challenges faced by Ethereum. The perseverance and vision of this team have propelled Arbitrum to the status of a major Layer 2 solution in the Ethereum ecosystem.

Technical Operation of Arbitrum
🔹 Utilization of Optimistic Rollup for Transaction Processing
Arbitrum operates using Optimistic Rollup technology, with a 2-step transaction processing process as seen in part 2.
🔹 Optimization of Fraud Management with an Advanced Proof System
Arbitrum goes further in optimizing fraud management. Its advanced proof system requires increased precision, specifically identifying the problematic transaction portion. This multi-round approach makes the fraud detection process faster and more cost-effective.
🔹 Introduction of the Arbitrum Virtual Machine (AVM) for Full Control over Transaction Execution
Arbitrum distinguishes itself by introducing its own virtual machine, the Arbitrum Virtual Machine (AVM). This innovation grants Arbitrum full control over transaction and smart contract execution. While this involves the need to translate application source code, the AVM offers increased flexibility in how transactions are processed.
🔹 Arbitrum and Programming Languages
Arbitrum integrates the following programming languages:
- Solidity (native integration on Arbitrum)
➮ Solidity is an object-oriented programming language used to develop smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain and other blockchains. Originally created by Gavin Wood (@gavofyork), co-founder and former CTO of Ethereum, the project began in 2014. Solidity draws inspiration from programming languages such as JavaScript, C++, and C# to facilitate adoption by developers.
➮ As an object-oriented language, Solidity enables interaction between objects, instances of concepts, or entities. It offers functionalities common to many languages, including function manipulation, structures, and strings. Further details on these features are available in Solidity’s official documentation.
➮ Solidity has been widely used in the development of numerous decentralized applications (dApps) on Ethereum, as well as in other projects such as a Proof of Concept (PoC) of SWIFT on a private blockchain called Borrow.
➮ Despite limited access to resources on Solidity in the past, it is now more accessible to learn to program in this language. The emergence of job postings requesting Solidity skills underscores its growing importance.
- Rust
Rust, a programming language favored by Amazon and Google, combines high performance and security. Open source and supported by the Rust Foundation, it effectively resolves memory errors, making it ideal for critical systems. Popular in gaming and virtual reality, Rust easily integrates with other languages. Cost-effective for open-source projects, it offers easy maintenance with its static typing and optimal performance without the need for continuous garbage collection. → Rust is the programming language used by Solana.
- C
The C language, created in the 1970s, is powerful, portable, and efficient. It provides direct memory control, enables structured programming, and remains fundamental in computer science, influencing many languages. → Its use of pointers offers flexibility but requires careful management. It is a preferred choice for applications requiring critical performance.
- C++
C++ is an evolution of the C language, incorporating object-oriented programming and offering high performance. → Versatile, it is widely used in fields such as video games and embedded systems. Its Standard Template Library (STL) facilitates development with ready-to-use data structures. In short, C++ combines efficiency and modularity.
➮ The last three languages mentioned (Rust, C, and C++) are integrated with Arbitrum Stylus. We’ll delve a bit more into what this entails in part 6.
➮ It’s also worth noting that Arbitrum is compatible with the EVM. In other words, dApps built on Ethereum can be “copy-pasted” onto Arbitrum.
The ARB Token and Governance
The $ARB token was introduced to the public during an airdrop in March 2023, marking a significant milestone in the evolution of Arbitrum.
🔹 Role of the ARB Token as a Governance Token
➮ The $ARB token is not limited to a transactional function; it holds a key role as a governance token. ARB holders have the power to participate in major decisions governing the Arbitrum protocol.
➮ $ARB also serves as a gas token. Yes, you heard that right! Many of you may not know, but @arbitrum recently developed a tool called Orbit for deploying Layer 3 solutions on Arbitrum. On these rollups of rollups, transaction fees are paid in $ARB.
🔹 Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO) Governance Mechanism
Arbitrum adopts a governance mechanism, a Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO). This approach allows ARB token holders to directly influence Arbitrum’s core code through votes. You can vote here: Arbitrum Foundation DAO Snapshot
🔹 Distribution of ARB Tokens and Roles of Holders in DAO Decisions
The distribution of ARB tokens reflects a balance between the community and key stakeholders. With majority control from the community, ARB token holders can decide on token allocation, ensuring democratic and participatory governance.
🔹 Tokenomics
Well, we think this is the part you’ve been waiting for the most, the famous tokenomics analysis!
➮ We will provide you with a pie chart showing the distribution of $ARB tokens.
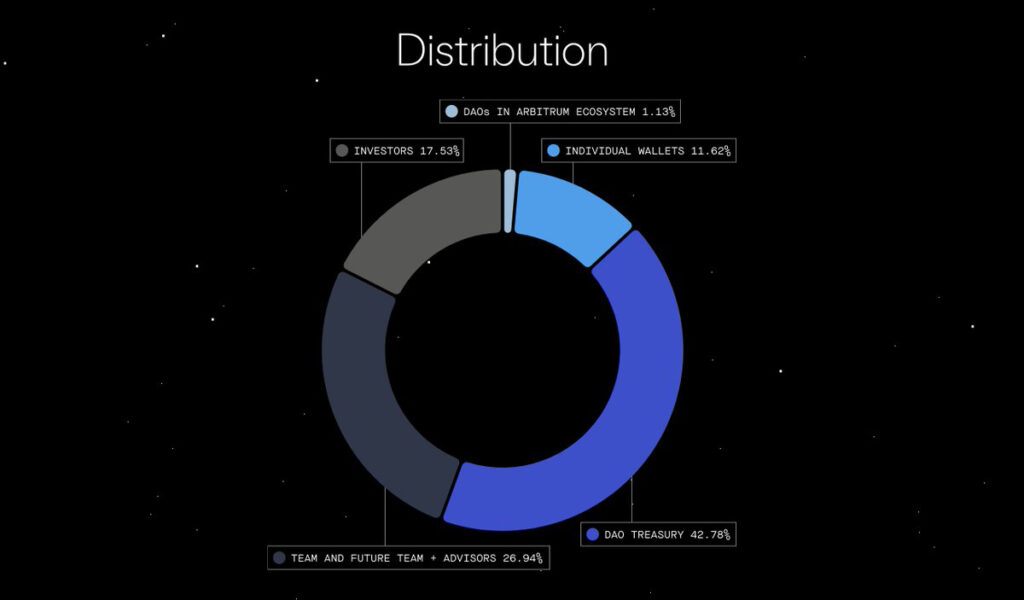
➮ I’m also providing you with a link to Token Unlock (an application providing extensive information on tokenomics, including token releases) : Token Unlock – Arbitrum
➮ as well as a link to CryptoRank (which is also an application providing extensive information on tokenomics and focusing on vesting, private investor statistics, etc.) : CryptoRank – Arbitrum
➮ Currently, only 15% of $ARB tokens are unlocked. Private investors and the team have their tokens under a Cliff (a waiting period during which $ARB tokens are gradually released). Recently, the DAO voted for the Arbitrum STIP. It’s a program aimed at releasing approximately 1% of tokens to attract new users to Arbitrum by offering $ARB to users in the Arbitrum ecosystem. There’s a lot of FUD (Fear, Uncertainty, Doubt) regarding ARB tokenomics. Many say that this token serves no purpose, but that’s not true. As we’ve seen before, it serves the DAO, pays gas fees on Layer 3…
The Arbitrum Ecosystem
🔹 Introduction to Various Products within the Ecosystem: Arbitrum One, Arbitrum Nova / Arbitrum AnyTrust, Arbitrum Nitro, Arbitrum Stylus, and Arbitrum Orbit.
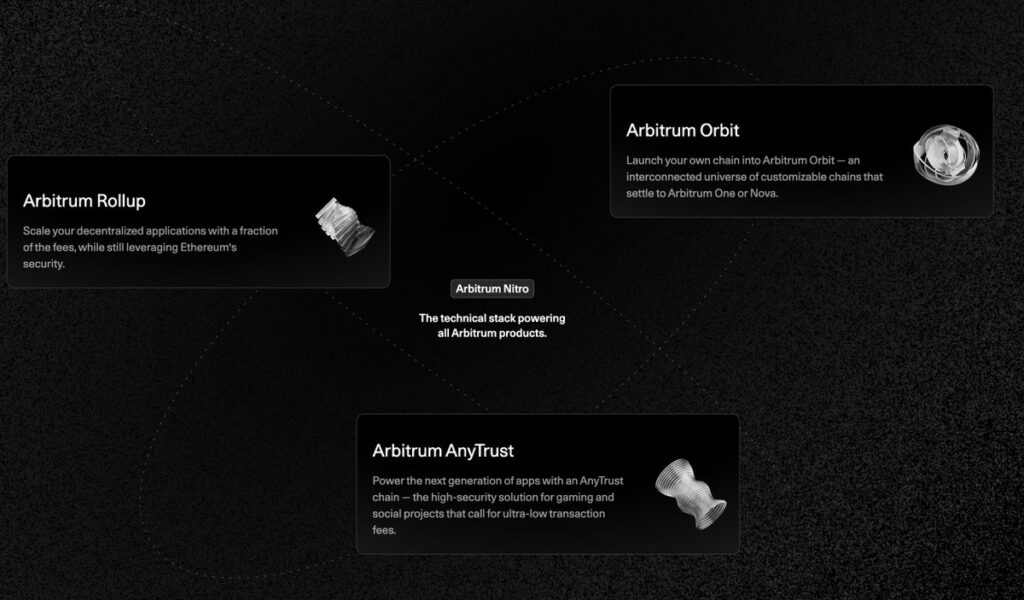
Arbitrum deploys a diverse ecosystem with several distinct products:
➮ Arbitrum One: This is the main network, benefiting from Ethereum Layer 1 security levels without relying on additional trust assumptions.
➮ Arbitrum Nova: An AnyTrust EVM equivalent solution, Arbitrum’s second mainnet rollup, tailored to projects sensitive to high transaction costs and volumes. On Arbitrum Nova, transaction fees are extremely low, and transactions are fast. Essentially, it’s a second-layer Arbitrum solution suited for enterprises and specifically for social networks and Web3 games requiring speed and low-cost transactions.
➮ Arbitrum Nitro: The technical software stack powering Arbitrum L2, making the rollup faster, cost-effective, and efficient, with the introduction of interactive proofs based on WebAssembly (“WASM”).
➮ Arbitrum Stylus: Arbitrum Stylus is an evolution of Arbitrum Nitro, introducing an EVM+ virtual machine that executes programs in WebAssembly (WASM). This upgrade provides developers with language flexibility, allowing the use of languages such as Rust, C, and C++, with improved performance compared to Solidity (as we saw in part 4). Stylus ensures security through Nitro technology and offers full interoperability between Solidity and WASM contracts. The development process involves coding, compiling into WASM, deployment on Arbitrum, and execution, providing significant gas savings.
➮ Arbitrum Orbit: An upcoming development framework facilitating the creation and deployment of Layer 3 solutions on top of the main Arbitrum network.
🔹 Advantages and Specificities of Each Product in Arbitrum’s Overall Strategy
Each product within the Arbitrum ecosystem addresses specific needs, thus contributing to an overarching strategy aimed at efficiency, economy, and adaptability. These diverse solutions enable Arbitrum to adapt to the varying requirements of projects and developers within the blockchain ecosystem.
Arbitrum’s Competitors
🔹 Arbitrum vs. Optimism: The Battle of Layer 2 Solutions on Ethereum
Let’s start by discussing the most prominent competitor: @Optimism.
➮ Over the past year, the Optimism and Arbitrum networks have seen significant growth within the Ethereum ecosystem as scaling solutions. While they share similarities, they also differ in several aspects.
- Similarities:
- Technology: Both rely on Optimistic Rollups, improving Ethereum network performance.
- Security: Ensure transaction security through their integration with Ethereum.
- Compatibility: Support Ethereum smart contracts, facilitating adoption by developers.
- Differences:
- Technical Architecture: Arbitrum adopts a modular architecture, offering more flexibility to developers. Optimism is based on “Bedrock,” focused on network efficiency.
- Sequencer Revenues: Optimism appears to have a slight advantage in terms of cumulative sequencer revenues, according to Delphi Digital.
- Recent Developments: Arbitrum launches “Arbitrum Orbit” for easy deployment of Layer 3 chains. Optimism releases “Bedrock,” improving transaction efficiency.
- Decentralization: Arbitrum seems to have better decentralization with a stronger DAO than Optimism.
- Future:
Success will depend on adoption by developers and users. While offering advantages, they will need to innovate to remain competitive, especially with the deployment of Ethereum 2.0 in 2022, which could influence the relevance of Layer 2 solutions. Arbitrum has a lead over Optimism, especially in terms of TVL, with twice as much Total Value Locked compared to its competitor and more users. In conclusion, Arbitrum and Optimism contribute to improving Ethereum’s performance, but their future depends on their ability to innovate in the face of competition and technological advancements. If we had to award the winner, we would give it to Arbitrum.
🔹 Other Competitors
Arbitrum has numerous other competitors, which essentially encompass all other Layer 2 solutions. Among them, we find:
➮ Starknet @Starknet $STARK: An L2 utilizing Zero-knowledge proof (ZK) technology.
➮ Manta @MantaNetwork $MANTA: A modular L2 utilizing Celestia for Data Availability and operating on Zero-knowledge proof.
➮ Scroll @Scroll_ZKP: Another Zero-knowledge proof Layer 2 as well.
There are many others, and you can explore them on this website that lists and categorizes them: https://l2beat.com/scaling/summary
In conclusion, Arbitrum emerges as a major pillar in the quest for blockchain scalability solutions. Its use of Optimistic Rollup, coupled with a talented team, demonstrates a strong commitment to improving the blockchain ecosystem. With its ARB token and decentralized governance, Arbitrum offers a promising outlook for the evolution of the sector. By positioning itself as a complement to Ethereum and offering a diverse range of products within its ecosystem, Arbitrum is actively shaping the future of blockchain scalability.


